Check out the latest update on how to leverage large language models (LLMs) to enhance your research, which has just been published by the Journal of Economic Literature:
We have witnessed remarkable advances in LLMs over the past six months as leading AI labs have outdone each other releasing increasingly powerful models. This update compiles the advances most relevant for researchers and focuses on two major breakthroughs: LLMs are learning to reason and to collaborate more effectively with researchers, making them increasingly useful.
#1 Breakthroughs in LLM-Based Reasoning
LLMs have become significantly more powerful at reasoning in recent months, resulting in impressive new capabilities in areas such as math and coding. Section 2.1 of my update explains how LLM-based reasoning models differ from traditional LLMs and approach complex problems by engaging in multi-step deliberations - thinking through problems similar to how human researchers would do it - before generating results. This is particularly valuable for:
Complex mathematical derivations (see Chat 1 in the paper, p. 10, for an example)
Sophisticated coding tasks (see Chat 2 in the paper, p. 13)
Multi-step problem solving
Error detection and correction
OpenAI's recently announced o3 reasoning model has achieved a milestone by surpassing 99.999% of humans - including most of us economists - in mathematical capabilities. Google has just released a similar model, while several Chinese labs have released open-source models with impressive reasoning capabilities. As one tech CEO noted, "intelligence is increasingly becoming a commodity."
For economists, this means that LLMs can now tackle previously challenging tasks like setting up and deriving theoretical models or writing complex code for economic analysis.
#2 Major Advances in LLM-Based Collaboration
A second major development are new ways to collaborate with LLMs, described in Section 2.2 of the update. Gone are the days of simple chat interfaces. New workspaces enable real-time, iterative collaboration - akin to working with a coauthor:
Anthropic's Claude Artifacts: Create and refine content in a dedicated workspace
ChatGPT's Canvas: Interactive document editing and coding
Microsoft Copilot & Google Workspace: AI integration in office tools
Cursor: Coding assistant
These tools transform how we interact with LLMs from one-off exchanges to dynamic collaborations where both human and AI contribute their strengths.
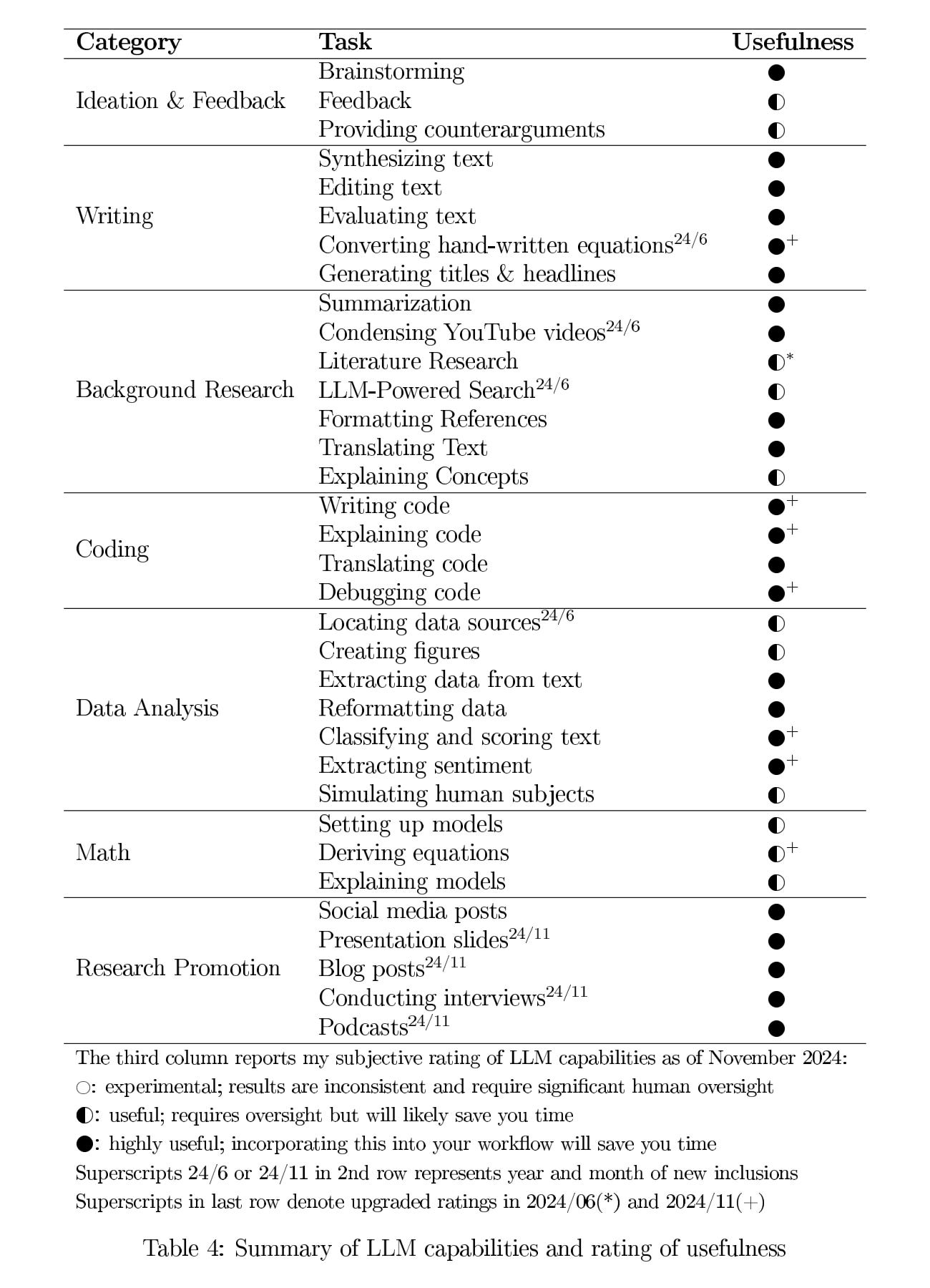
Comprehensive Capability Assessment
To help researchers navigate these advances, I have compiled a comprehensive assessment of LLM capabilities across seven domains. The table below evaluates three dozen different use cases, from ideation and writing to coding and mathematical derivations:
I encourage readers to use this as a checklist to explore which capabilities they have already incorporated into their workflow and which ones might offer new opportunities to enhance their research productivity. Many capabilities that were experimental just months ago are now highly reliable, particularly in areas like coding and data analysis.
Additional Advances
The update also covers several other significant developments:
LLM-powered search tools that combine web access with AI synthesis
Improved abilities to handle research promotion tasks, including generating presentations and podcasts
Real-time voice assistants for fluid interaction
Significant cost reductions and efficiency gains across all major providers
Looking Ahead
The rapid advances of the past six months contribute to an ongoing paradigm shift in how we conduct economic research. While LLMs initially served just as helpful assistants for specific micro-tasks in 2023, they are now evolving into sophisticated research collaborators capable of both independent reasoning and dynamic interaction.
The advances described in this update represent a significant opportunity to enhance research productivity. I encourage readers to experiment with these capabilities - starting with the ones rated as "highly useful" in the table - and find ways to incorporate them into their research workflow while maintaining the highest standards of academic integrity. Ultimately, when used thoughtfully, these tools enhance our ability to fulfill our professional mission of generating and sharing economic insights that benefit society.
The full update explores these developments in detail, including specific examples and use cases. You can access it here:
As always, I welcome your feedback and suggestions. Please share your own experiences with LLMs and your thoughts on these developments, send me any examples of use cases that you were impressed by, or suggest areas you'd like to see covered in future updates!
Thanks for reading Updates - Generative AI for Economic Research. If you find these updates useful, please recommend them to your colleagues and coauthors.