The landscape of generative AI has evolved rapidly since the publication of the original published version of Generative AI for Economic Research (JEL, 2023).
Recent progress in LLMs has been characterized by better performance, growing context windows so LLMs can process more data at once, better recall, faster processing, and falling costs—all music to the ears of economists. Taken together, these changes have also led to qualitatively new ways of applying LLMs in research.
The three leading frontier AI labs have each released significant updates to their LLM offerings incorporating, among other features, vision capabilities and real-time sound processing. As of my editorial deadline in May 2024, OpenAI's GPT-4o, was the best available LLM, powering the popular ChatGPT service. Yet in June 2024, Anthropic released its Claude 3.5 Sonnet model, which is currently the most powerful publicly available LLM, and the one I use the most. One of my favorite aspects of it is the new “Artifacts” feature that makes it easier to use AI as a writing and thinking partner:
(For instructions on how to enable Artifacts in Claude see the beginning of this.)
Moreover, I regularly use Google DeepMind’s Gemini Pro 1.5, released in January 2024, which currently offers the largest context window—the publicly available version can process up to 1m tokens (about 1500 pages of text) simultaneously.
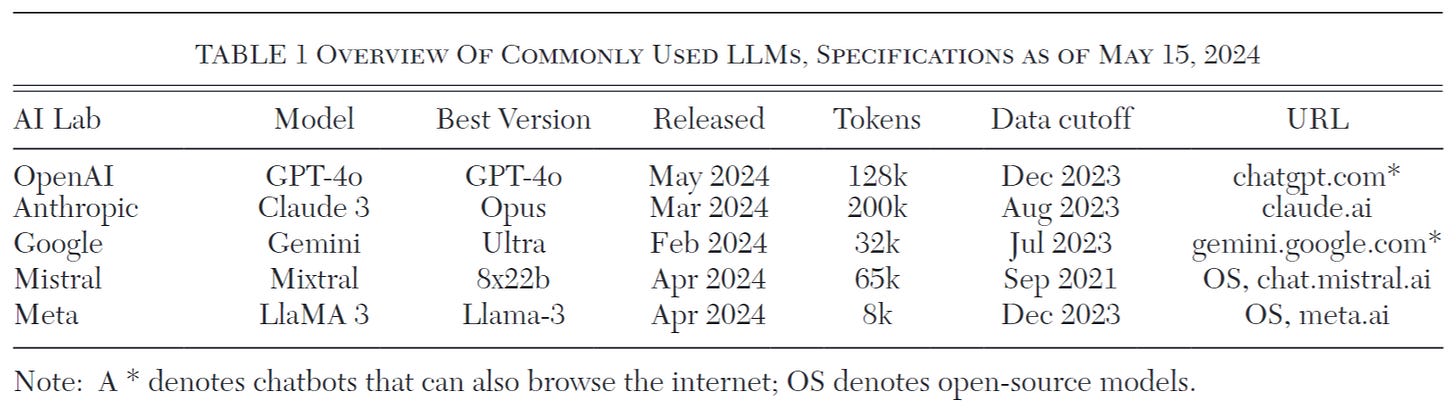
Whereas the described frontier models are proprietary and only available via the Internet, a growing number of smaller (albeit less capable) models have been released open-source, allowing users to employ them on their own servers for security- or privacy-sensitive applications, for example Meta’s LlaMA 3 or Mixtral 8x22b. Some open source models are small enough that they can be run on laptops and even cell phones. Here is an overview table from the paper:
In addition to describing these new developments in the update, I also cover several novel examples and use cases for LLMs:
Automated prompt generation
Feedback on research via voice chats
Converting hand-written equations to LaTeX
Generating presentation slides
Summarizing YouTube videos
Outlining a plan for a coding project
Finding data sources
The update also discusses the four emerging ways to interact with LLMs (web-based chatbots, real-time voice assistants, web-based experimentation platforms, APIs) and how to use ChatGPT and Claude while maintaining data confidentiality.
To access the official 2024Q2 JEL update, simply click the following button:
(The manuscript version of the update is also available in PDF format here.)
Thank you for following my updates. Please share your feedback and suggestions for additional use cases and future updates below or via email to akorinek@virginia.edu.